計畫名稱 : 綠廠房資訊模擬與智慧監測應用技術開發
計畫緣起:
台灣目前是全球最大之晶圓產能供應國,占全球晶圓產能的21%,同時台灣也是擁有最多具競爭優勢的12吋晶圓廠。而半導體晶圓之研發製造必須在高品質的廠房裡,於嚴格環境控制的潔淨室(Cleanroom)中進行,同時,為促使產品儘早進入市場,更必須儘早完成廠房之建置。根據2011國際半導體技術路徑(International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductor, ITRS) 之報告指出,國際半導體及相關產業之製程技術,將從2014年開始進入18吋晶圓之量產,並預計於2017年開始進入閘寬(Gate Length)14奈米之製程。而廠房從施工興建至開始裝設生產設備,也估計於九個月內完成,因此提升台灣半導體廠房之規劃、設計、建造、環境監控的品質及效率為目前相當重要之課題。
同時,由於生產環境精密控制的要求,半導體廠房之生產消耗大量的能源,衍生大量在背後為生產所需的相對能源之二氧化碳,導致破壞生態環境系統。因此,如何能夠最有效的使用能源,如何透過智慧監測來節能減碳、保護生態環境的綠廠房,亦是未來半導體產業研究之主要課題。
計畫摘要(包括計畫架構圖,重要工作或目標)
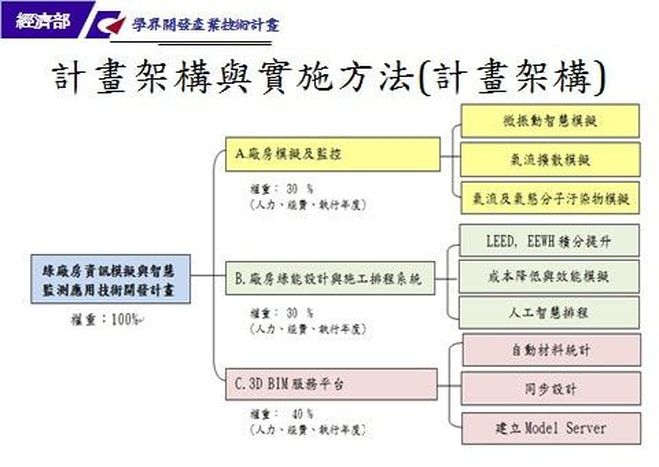
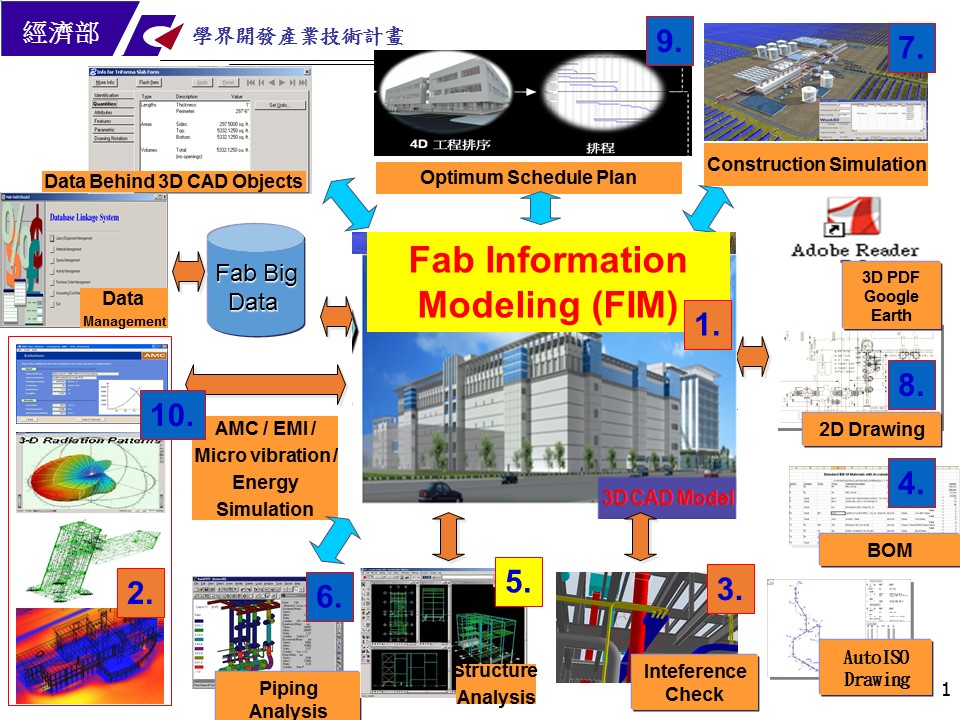
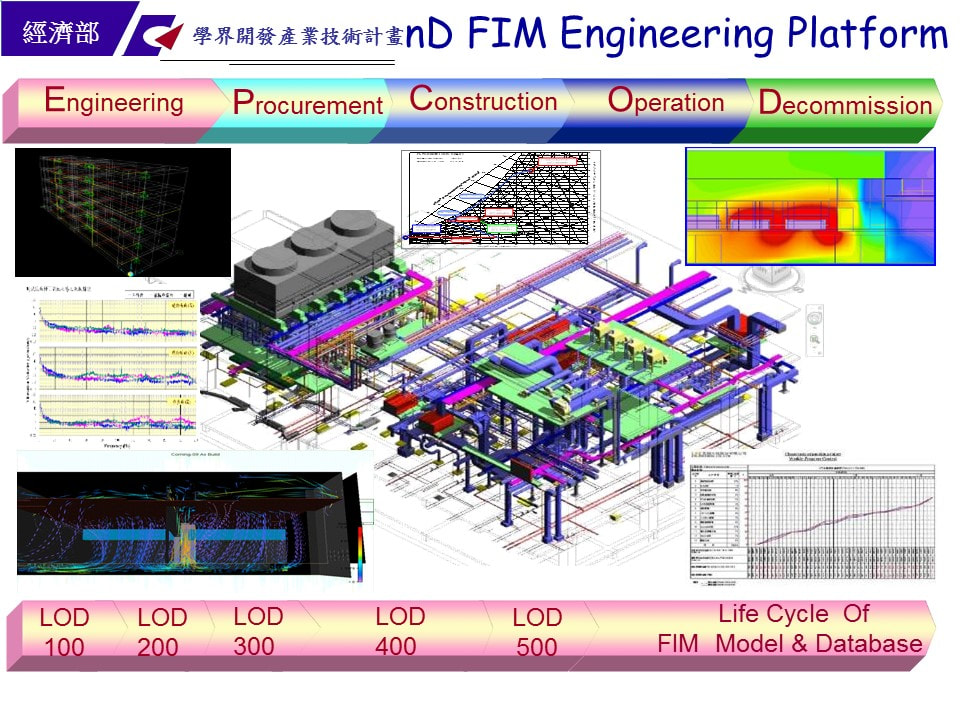
本計畫總體目標旨在開發一綠廠房資訊模擬與智慧監測應用技術,運用開發出來的智慧技術應用服務到半導體廠房生命週期之規劃、設計、興建、採購、試車、移交、營運、保養、維修及監控。本團隊之計畫架構圖及重要工作,詳下圖。
計畫緣起:
台灣目前是全球最大之晶圓產能供應國,占全球晶圓產能的21%,同時台灣也是擁有最多具競爭優勢的12吋晶圓廠。而半導體晶圓之研發製造必須在高品質的廠房裡,於嚴格環境控制的潔淨室(Cleanroom)中進行,同時,為促使產品儘早進入市場,更必須儘早完成廠房之建置。根據2011國際半導體技術路徑(International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductor, ITRS) 之報告指出,國際半導體及相關產業之製程技術,將從2014年開始進入18吋晶圓之量產,並預計於2017年開始進入閘寬(Gate Length)14奈米之製程。而廠房從施工興建至開始裝設生產設備,也估計於九個月內完成,因此提升台灣半導體廠房之規劃、設計、建造、環境監控的品質及效率為目前相當重要之課題。
同時,由於生產環境精密控制的要求,半導體廠房之生產消耗大量的能源,衍生大量在背後為生產所需的相對能源之二氧化碳,導致破壞生態環境系統。因此,如何能夠最有效的使用能源,如何透過智慧監測來節能減碳、保護生態環境的綠廠房,亦是未來半導體產業研究之主要課題。
計畫摘要(包括計畫架構圖,重要工作或目標)
本計畫總體目標旨在開發一綠廠房資訊模擬與智慧監測應用技術,運用開發出來的智慧技術應用服務到半導體廠房生命週期之規劃、設計、興建、採購、試車、移交、營運、保養、維修及監控。本團隊之計畫架構圖及重要工作,詳下圖。
Project : Automated Digital Color Image Processing for Coating Quality
Abstrac:
Previously developed image recognition methods by the Principal Investigator (PI) and his former Ph.D. students for rust defect assessment can be summarized as two: the NFRA (Neuro-Fuzzy Recognition Approach) method and the SKMA (Simplified K-Means algorithm) method. The NFRA method uses artificial intelligence techniques to separate rust pixels from background pixels. The SKMA method segments object pixels and background pixels in a digitized image using a statistical method, called the K-means algorithm. Even if both methods pass through different processing procedures, one common thing is that they first convert original color images to grayscale images and further process the grayscale images. They do not process color image directly.
The system are often encountered difficulties while acquiring digital images under environmental conditions such as non-uniform illuminations, low-contrast digital images, and noises on painting surfaces. The purpose of this proposal is to explore the use of color space theories for processing digital color image and developing an automated system on controlling coating quality.
The rust defect assessment system will be realized by passing through seven steps: 1) steel bridge coating image, 2) optimal color space, 3) coordinate system adjustment, 4) histogram generation, 5) separation of target areas, 6) image reconstruction, and 7) assessment of defects.
Abstrac:
Previously developed image recognition methods by the Principal Investigator (PI) and his former Ph.D. students for rust defect assessment can be summarized as two: the NFRA (Neuro-Fuzzy Recognition Approach) method and the SKMA (Simplified K-Means algorithm) method. The NFRA method uses artificial intelligence techniques to separate rust pixels from background pixels. The SKMA method segments object pixels and background pixels in a digitized image using a statistical method, called the K-means algorithm. Even if both methods pass through different processing procedures, one common thing is that they first convert original color images to grayscale images and further process the grayscale images. They do not process color image directly.
The system are often encountered difficulties while acquiring digital images under environmental conditions such as non-uniform illuminations, low-contrast digital images, and noises on painting surfaces. The purpose of this proposal is to explore the use of color space theories for processing digital color image and developing an automated system on controlling coating quality.
The rust defect assessment system will be realized by passing through seven steps: 1) steel bridge coating image, 2) optimal color space, 3) coordinate system adjustment, 4) histogram generation, 5) separation of target areas, 6) image reconstruction, and 7) assessment of defects.